How To Find the Default Block Size in Unix
The questions about default block sizes used in your Unix system are always popular. Today I’d like to show you a few ways to answer them.
Default block size in Linux
If you ever want to confirm the block size of any filesystem of Ubuntu or any other Linux OS, tune2fs command is here to help:
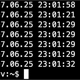
ubuntu# tune2fs -l /dev/sda1 | grep Block
Block count: 4980736
Block size: 4096
Blocks per group: 32768From this example, you can see that the default block size for the filesystem on /dev/sda1 partition is 4096 bytes, or 4k. That’s the default block size for ext3 filesystem.
Default block size in Solaris
The default block size in Solaris is 8192 bytes, or 8k. However, some architectures allow you to use 4k size as well, by specifying it as a command line option for the newfs command.
To be absolutely sure, you can use one of the commands: df -g (takes a filesystem mount point name as the parameter – / or /usr for example) or use fstyp -v command (needs a character device of the filesystem you’re interested in).
Using df -g to confirm the filesystem block size
This command can be used as any user, so to confirm a block size for any of the filesystems you don’t have to be root. However, it works only for mounted filesystems.
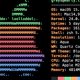
bash-3.00$ df -g /
/ (/dev/dsk/c1t0d0s0 ): 8192 block size 1024 frag size
12405898 total blocks 4399080 free blocks 4275022 available 751296 total files
603544 free files 30932992 filesys id
ufs fstype 0x00000004 flag 255 filename lengthUsing fstyp -v to confirm the filesystem block size
Because this command accesses the character device of a particular filesystem, you have to be root to run it. But as a bonus compared to df -g, you can use fstyp -v on an unmounted filesystem:
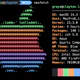
bash-3.00# fstyp -v /dev/dsk/c1t0d0s0 | grep ^bsize
bsize 8192 shift 13 mask 0xffffe000