mv – move and rename files
mv moves or renames files and directories. Unlike cp, it doesn’t create a copy — the original is removed.
Synopsis
mv [OPTIONS] SOURCE DEST
mv [OPTIONS] SOURCE... DIRECTORY
Common Options
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-i | Prompt before overwriting |
-n | Don’t overwrite existing files |
-f | Force overwrite without prompting |
-u | Move only when source is newer |
-v | Verbose, show files being moved |
--backup | Create backup of destination files |
Examples
Rename a file
$ mv oldname.txt newname.txt
Move file to directory
$ mv file.txt /tmp/
$ mv file.txt /tmp/newname.txt
Move multiple files
$ mv file1.txt file2.txt file3.txt /backup/
$ mv *.log /var/log/archive/
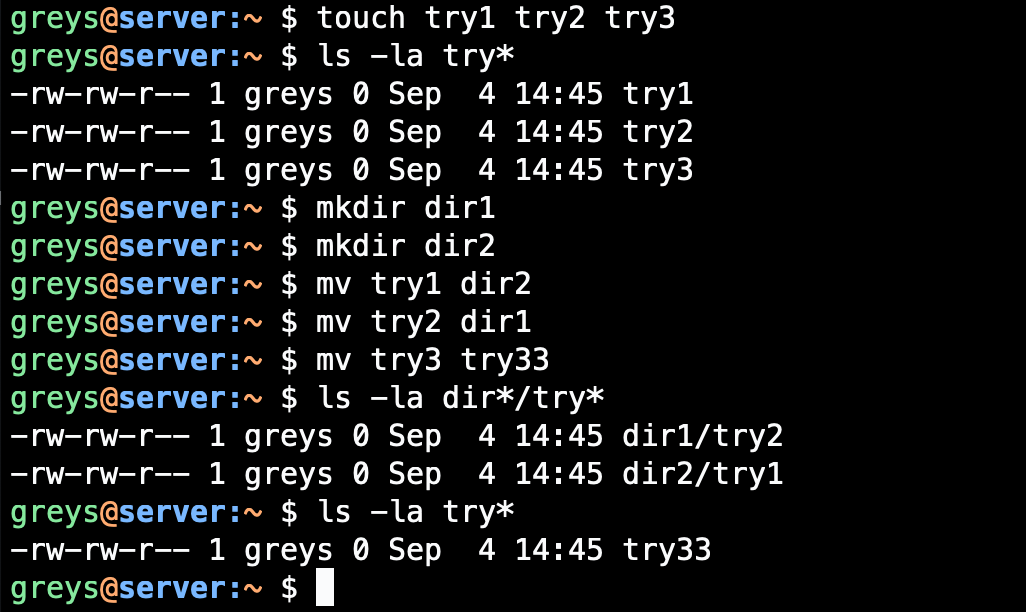
Move directory
$ mv project/ archived_project/
Interactive mode (ask before overwriting)
$ mv -i source.txt dest.txt
mv: overwrite 'dest.txt'? y
Don’t overwrite existing
$ mv -n newfile.txt existing.txt
# No error, existing.txt unchanged
Verbose output
$ mv -v *.txt archive/
'file1.txt' -> 'archive/file1.txt'
'file2.txt' -> 'archive/file2.txt'
Create backup when overwriting
$ mv --backup=numbered file.txt /dest/
# Creates file.txt.~1~ if file.txt exists in /dest/
Move only if source is newer
$ mv -u updated.txt /dest/
Common Patterns
Rename with date stamp
$ mv report.txt report-$(date +%Y%m%d).txt
Batch rename (lowercase to uppercase)
$ for f in *.txt; do mv "$f" "${f^^}"; done
Move and rename simultaneously
$ mv dir1/oldfile.txt dir2/newfile.txt
Swap two files
$ mv file1.txt tmp.txt
$ mv file2.txt file1.txt
$ mv tmp.txt file2.txt
Move vs Rename
When source and destination are on the same filesystem:
- Fast — just updates directory entries (no data copy)
When on different filesystems:
- Slower — actually copies data, then removes original
# Same filesystem = instant
$ mv /home/user/file.txt /home/user/backup/
# Different filesystem = copy + delete
$ mv /home/user/file.txt /mnt/usb/
Tips
- Use -i by default: Add
alias mv='mv -i'to ~/.bashrc - No undo: mv doesn’t have a trash — be careful!
- Rename directories the same way as files
- For complex renames: Use
renamecommand or a loop - Atomic on same FS: mv is safe for log rotation
See Also
Related Commands
- cp — Copy files (keeps original)
- rm — Remove files
- rename — Batch rename with patterns
- ls — List directory contents