head – output the first part of files
head displays the first lines of a file. By default, it shows the first 10 lines.
Synopsis
head [OPTIONS] [FILE...]
Common Options
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-n N | Show first N lines |
-c N | Show first N bytes |
-q | Quiet, don’t print headers for multiple files |
-v | Always print headers |
Examples
Show first 10 lines (default)
$ head /var/log/syslog
Jan 15 00:00:01 server CRON[1234]: ...
Jan 15 00:00:02 server systemd[1]: ...
...
Show first N lines
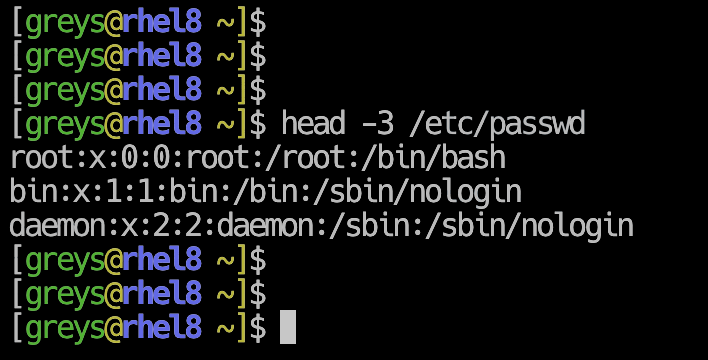
$ head -n 5 /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
daemon:x:1:1:daemon:/usr/sbin:/usr/sbin/nologin
bin:x:2:2:bin:/bin:/usr/sbin/nologin
sys:x:3:3:sys:/dev:/usr/sbin/nologin
sync:x:4:65534:sync:/bin:/bin/sync
Show first N bytes
$ head -c 100 file.txt
Multiple files
$ head -n 3 file1.txt file2.txt
==> file1.txt <==
Line 1
Line 2
Line 3
==> file2.txt <==
First line
Second line
Third line
Combine with other commands
$ ls -lt | head -n 5 # 5 most recently modified
$ ps aux | head -n 10 # First 10 processes
$ history | head -n 20 # First 20 commands
Show all but last N lines
$ head -n -5 file.txt # All lines except last 5
Tips
- Quick file preview:
head file.txtbefore opening large files - CSV headers:
head -n 1 data.csvto see column names - Combine with tail:
head -n 100 | tail -n 10for lines 91-100 - Watch growing files: Use
tail -finstead for live updates
See Also
Related Commands
- tail — Show last lines of file
- cat — Show entire file
- less — Interactive file viewer
- more — Simple pager